Introduction
Understanding the Nervous System
The nervous system is an intricate network of specialized cells called neurons that coordinate and regulate bodily functions. It’s essentially the body’s communication system, allowing for rapid and efficient responses to both internal and external stimuli. This complex system is responsible for everything from simple reflexes to conscious thought and movement.
Divisions of the Nervous System
The nervous system can be broadly divided into two main parts:
-
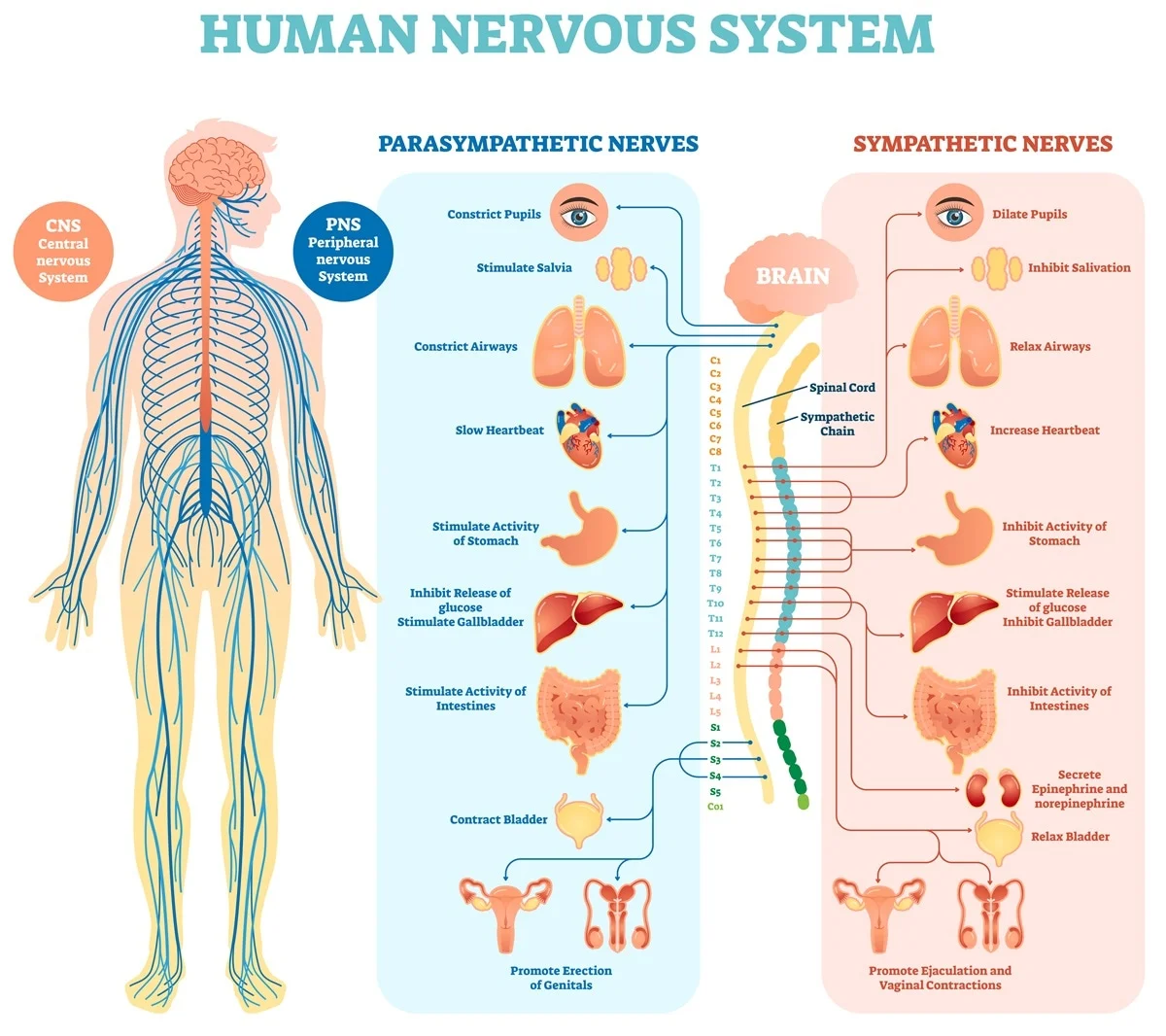
Central Nervous System (CNS):
- Brain: The control center, responsible for processing information, initiating responses, and storing memories.
- Spinal Cord: Connects the brain to the rest of the body, transmitting signals between the brain and the peripheral nervous system.
-
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS):
- Somatic Nervous System: Controls voluntary muscle movements.
- Autonomic Nervous System: Regulates involuntary functions like heart rate, digestion, and respiration.
- Sympathetic Nervous System: Prepares the body for action (fight-or-flight response).
- Parasympathetic Nervous System: Promotes relaxation and recovery (rest-and-digest response).
How Neurons Communicate
Neurons communicate through electrical and chemical signals. When a neuron is stimulated, an electrical impulse travels down its axon (a long, thin fiber). At the end of the axon, neurotransmitters (chemical messengers) are released, crossing the synapse (the gap between neurons) to bind with receptors on the next neuron. This process, known as neurotransmission, allows information to be passed from one neuron to another.
Functions of the Nervous System
The nervous system performs a multitude of vital functions, including:
- Sensory Perception: Gathering information from the environment through the senses (sight, hearing, touch, taste, smell).
- Motor Control: Coordinating movement and muscle activity.
- Homeostasis: Maintaining a stable internal environment.
- Cognition: Thinking, learning, memory, and problem-solving.
- Emotion: Experiencing and expressing feelings.
Disorders of the Nervous System
Numerous conditions can affect the nervous system, ranging from mild to severe. Some common disorders include:
- Neurodegenerative diseases: Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, multiple sclerosis.
- Mental health disorders: Depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder.
- Pain conditions: Migraines, back pain, neuropathy.
- Brain injuries: Concussions, traumatic brain injury.
- Stroke: Disruption of blood flow to the brain.
Protecting Your Nervous System
To maintain a healthy nervous system, consider the following tips:
- Balanced diet: Provide essential nutrients for brain health.
- Regular exercise: Improves blood flow and cognitive function.
- Adequate sleep: Essential for brain repair and consolidation of memories.
- Stress management: Reduces the impact of stress on the nervous system.
- Avoid harmful substances: Limit alcohol, tobacco, and illicit drugs.
Conclusion
The nervous system is a marvel of biological engineering, responsible for every thought, feeling, and action. Understanding its structure and function can help you appreciate its complexity and take steps to protect it.


0 Comments